Rare Flora
Nepal's diverse ecosystems, ranging from the steamy Terai lowlands to the frosty peaks of the Himalayas, create a unique haven for a variety of rare and exotic flora. Here are some highlights of Nepal's rare flora that underscore its status as a biodiversity hotspot:

-
Nepal Rhododendrons: Nepal is home to over 30 species of rhododendrons, some of which are endemic to the region. These plants light up the Himalayan landscape with their vibrant blooms in spring, ranging from whites and pinks to deep reds. The national flower of Nepal, the Lali Gurans, is a particularly famous rhododendron species known for its striking beauty.
-
Nepal Orchids: With more than 370 identified species, the orchids of Nepal are a symbol of its botanical richness. These include both terrestrial and epiphytic species, found in various habitats from the lowland jungles to the cloud forests. The diversity in orchids is particularly notable in the regions of Annapurna, Langtang, and Everest.
-
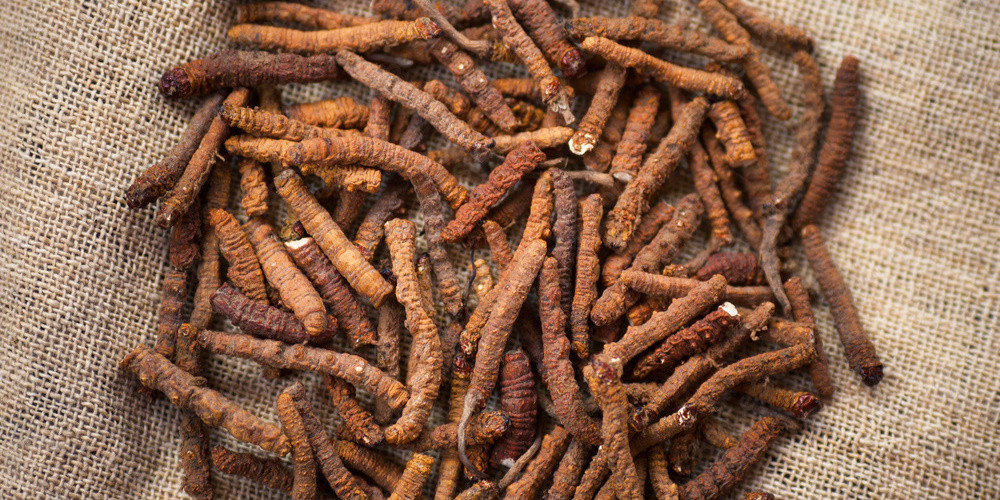
Yarsagumba (Cordyceps sinensis): Perhaps one of the most intriguing of Nepal's flora, Yarsagumba, or the "Himalayan Viagra," is a rare caterpillar-fungus hybrid. It grows in the meadows of Nepal's high Himalayas. Valued for its medicinal properties, it has become a significant source of income for local communities, although overharvesting is a concern for conservationists.
-
Himalayan Blue Poppy (Meconopsis spp.): Among the alpine treasures of Nepal, the Himalayan Blue Poppy stands out with its mesmerizing blue flowers. It thrives in the moist, cool climate of the high mountains and is often sought after by trekkers for its unique beauty.
-
Aconitum spicatum (Bikh, Vatsanabhi): Aconitum spicatum is a species of monkshood found in the Himalayas of Nepal, known for its potent medicinal properties as well as its toxicity. It is used in traditional medicine but must be handled with care.
Conservation and Challenges
The conservation of these rare flora species is critical, not just for the sake of preserving biodiversity, but also for maintaining the ecological balance and supporting local communities dependent on them. Challenges such as habitat destruction, climate change, and overharvesting threaten Nepal's botanical treasures. Efforts are ongoing to protect these species through various conservation strategies, including the establishment of protected areas, community forests, and the promotion of sustainable harvesting practices.
Nepal's rich floral diversity is a crucial part of its natural heritage. Preserving this treasure not only supports ecological health and local economies but also contributes to global biodiversity.
Rare Fauna
Nepal's varied landscapes, from the lush Terai plains to the rugged Himalayan highlands, provide habitats for an array of rare and endangered fauna. These species not only contribute to the ecological diversity but also hold significant cultural and economic value. Here are some highlights of the rare fauna found in Nepal:

-
Snow Leopard (Panthera uncia): The elusive Snow Leopard is a symbol of the Himalayan wilderness, found in the high-altitude regions of Nepal. Adapted to living in harsh, cold environments, snow leopards are a key indicator of the health of mountain ecosystems. Despite their elusive nature, they face threats from poaching, loss of prey, and habitat destruction.
-
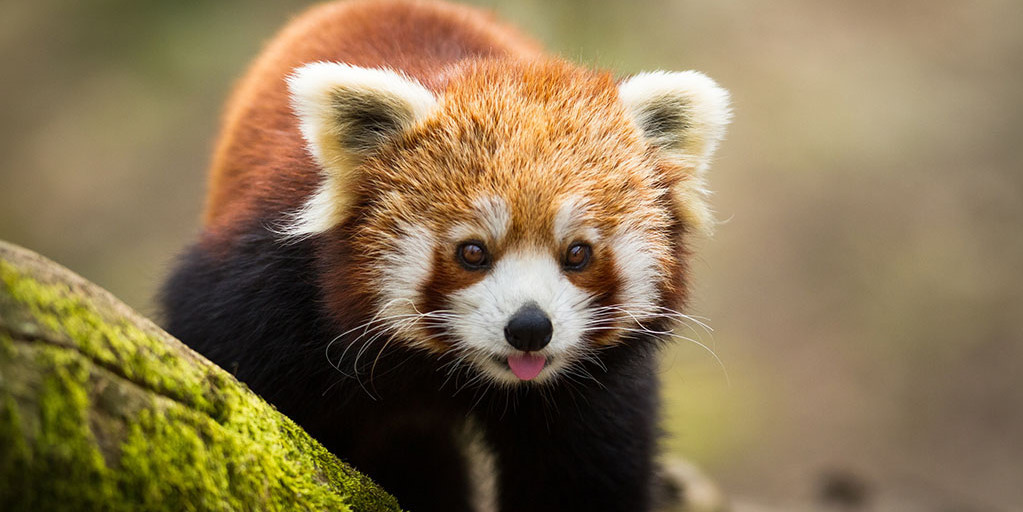
Red Panda (Ailurus fulgens): The Red Panda, with its distinctive reddish-brown fur and bushy tail, inhabits the bamboo forests of eastern Nepal. This adorable mammal is under threat due to deforestation, habitat fragmentation, and poaching. Conservation efforts in Nepal focus on protecting its habitat and raising awareness of its plight.
-
Bengal Tiger (Panthera tigris tigris): Nepal's Terai region provides a critical habitat for the Bengal Tiger, one of the most revered and iconic big cats in the world. Through successful conservation initiatives, including anti-poaching efforts and habitat restoration, Nepal has seen a gradual increase in tiger populations, showcasing a global conservation success story.
-
One-horned Rhinoceros (Rhinoceros unicornis): The One-horned Rhinoceros is primarily found in the grasslands and forests of Chitwan and Bardia National Parks. Once close to extinction, concerted conservation efforts in Nepal, including strict anti-poaching measures and habitat management, have significantly increased their numbers.
-
Gharial (Gavialis gangeticus): The Gharial, a critically endangered crocodile species, is known for its distinctive long, narrow snout. Nepal's conservation programs, especially in the Chitwan National Park, focus on the protection and breeding of gharials to prevent their extinction.
-
Himalayan Musk Deer (Moschus leucogaster): The Himalayan Musk Deer is sought after for its musk pod, used in traditional medicines and perfumes, leading to overhunting. Found in the forested and alpine regions of Nepal, conservation efforts aim to protect this species from poaching and habitat loss.
Conservation Efforts and Challenges
Nepal's approach to wildlife conservation is multifaceted, involving habitat protection, anti-poaching patrols, and community-based conservation projects. Despite these efforts, many of Nepal's rare fauna continue to face threats from human activities, including habitat encroachment, poaching, and climate change. Strengthening conservation initiatives, enhancing legal frameworks, and promoting sustainable tourism are key to ensuring the survival of these unique species.
Nepal's rare fauna are a vital part of its natural heritage and biodiversity. Protecting these species and their habitats not only benefits Nepal but contributes to global biodiversity conservation efforts. Through continued dedication to conservation and sustainable practices, Nepal aims to safeguard these treasures for future generations.
Nepal's vast array of rare flora and fauna is a vivid testament to the country's rich biodiversity, making it a vital part of the global natural heritage. From the majestic snow leopards and Bengal tigers to the endemic rhododendrons and the medicinal Yarsagumba, Nepal's biodiversity is both a source of national pride and a critical ecological asset. The nation's commitment to conservation, through national parks, wildlife reserves, and community-led efforts, highlights the importance of preserving these natural treasures. However, challenges like habitat destruction and climate change underscore the need for ongoing vigilance and global cooperation in conservation efforts. As a beacon of biodiversity, Nepal reminds us of the importance of sustaining our planet's natural diversity for future generations, emphasizing our collective responsibility to protect and cherish these rare and precious gifts of nature.
FAQs for Rare Flora and Fauna in Nepal: A Treasure Trove of Biodiversity
Q: What factors contribute to Nepal's status as a hotspot for rare flora and fauna?
A: Nepal's diverse topography, ranging from lowland plains to Himalayan peaks, coupled with its unique geographical location between the Indian subcontinent and the Tibetan plateau, create varied habitats conducive to a wide array of plant and animal species.
Q: Can you name a few rare plant species indigenous to Nepal?
A: Certainly. Some notable rare plant species found in Nepal include the Himalayan blue poppy (Meconopsis grandis), the national flower rhododendron (Rhododendron arboreum), the aromatic spikenard (Nardostachys grandiflora), and the medicinal yarsagumba (Ophiocordyceps sinensis).
Q: What are some iconic animal species that call Nepal home?
A: Nepal is renowned for its diverse wildlife, which includes iconic species such as the Bengal tiger (Panthera tigris tigris), the one-horned rhinoceros (Rhinoceros unicornis), the elusive snow leopard (Panthera uncia), and the charming red panda (Ailurus fulgens).
Q: How does Nepal strive to conserve its rare flora and fauna?
A: Nepal employs a variety of conservation strategies, including the establishment of protected areas, community-based conservation initiatives, anti-poaching measures, sustainable tourism practices, and collaborations with international organizations and governmental agencies.
Q: What are some of the challenges Nepal faces in conserving its biodiversity?
A: Nepal faces challenges such as habitat loss due to deforestation and urbanization, poaching, illegal wildlife trade, human-wildlife conflict, and the impacts of climate change, all of which threaten the survival of rare flora and fauna.
Q: How can individuals contribute to the conservation of Nepal's biodiversity?
A: Individuals can support conservation efforts by practicing responsible tourism, respecting wildlife habitats, promoting sustainable lifestyles, supporting local conservation initiatives, advocating for wildlife protection policies, and raising awareness about the importance of biodiversity conservation.
Q: Are there any specific endangered species conservation programs in Nepal?
A: Yes, Nepal has several conservation programs dedicated to protecting endangered species, including the National Rhino Conservation Strategy for the conservation of one-horned rhinoceros and the Snow Leopard Conservation Action Plan to safeguard the elusive snow leopard population.
Q: How does climate change impact Nepal's rare flora and fauna?
A: Climate change poses significant threats to Nepal's biodiversity by altering habitats, disrupting ecosystems, and affecting the distribution and behavior of plant and animal species, thereby exacerbating existing conservation challenges.
Q. Question: What role do local communities play in biodiversity conservation in Nepal?
A: Local communities in Nepal often serve as key stakeholders in biodiversity conservation through their participation in community-based conservation projects, sustainable resource management practices, and ecotourism initiatives that contribute to both conservation efforts and community development.
Q: Question: How does Nepal balance conservation efforts with the needs of its growing population?
A: Nepal employs integrated conservation and development approaches that aim to balance biodiversity conservation with sustainable development by promoting community participation, implementing ecosystem-based management strategies, and fostering cooperation between conservation organisations, governmental agencies, and local communities.
For the Nepal Tour ideas and suggestions.
If you are looking for different kinds of Nepal Packages, feel free to contact us.
.jpg)